Have you ever noticed that even when your website is technically optimized and has relevant backlinks, you still have trouble with website traffic?
What a lot of people don’t realize is that duplicate content might be part of the problem. And no, it doesn’t mean you copied anything on purpose. Sometimes it’s unintentional and happens more often than you’d think.
In this article, we will provide our expert insights on how to identify and avoid duplicate content issues with quick, beginner-friendly tips and steps.
Let’s go!
What is Duplicate Content?
Duplicate content is pieces of the same information written on two or more web pages. This can happen in blog pages, service and landing pages, or other documentation on the website.
In most cases, duplicate content is caused by minor technical issues, such as editors posting the same article twice or having two versions of the same page with different URLs.
It doesn’t seem to be a big issue, but once you read further, you will find out how it impacts your rankings significantly.
How Does Duplicate Content Hurt Your SEO?
Beyond causing a significant drop in traffic, it can also lead to:
- Search engine confusion: When multiple pages have the same content, Google and other search engines struggle to decide which one to rank.
- Wasted crawl budget: Search engines may waste time indexing duplicate pages instead of focusing on your fresh, valuable content.
- Poor user experience: Visitors expecting new or unique information may feel disappointed when they see similar content.
- Higher exit rates: If users don’t find what they’re looking for, they’re more likely to leave your site quickly, resulting in higher bounce and exit rates.
Luckily, handling duplicates is easier than you think. As a first step, let’s see what tools our SEO specialists recommend for identifying duplicates.
Our Top Tools to Find Duplicate Content
Detecting duplicate content manually can take time and resources. The good news is that there are millions of free tools on the web that help SEOs quickly identify issues.
Below, we have highlighted the two main tools that we use, and you can too.
Siteliner
Siteliner is one of the main tools used for conducting a website audit, including checking for duplicate content. Here are some simple steps to get started:
- Go to Siteliner.com and input your website URL.
- Once the tool finishes scanning your website, click on the “Duplicate content” tab and see the list of your website’s pages with matching content, along with the percentage of duplication for each URL.
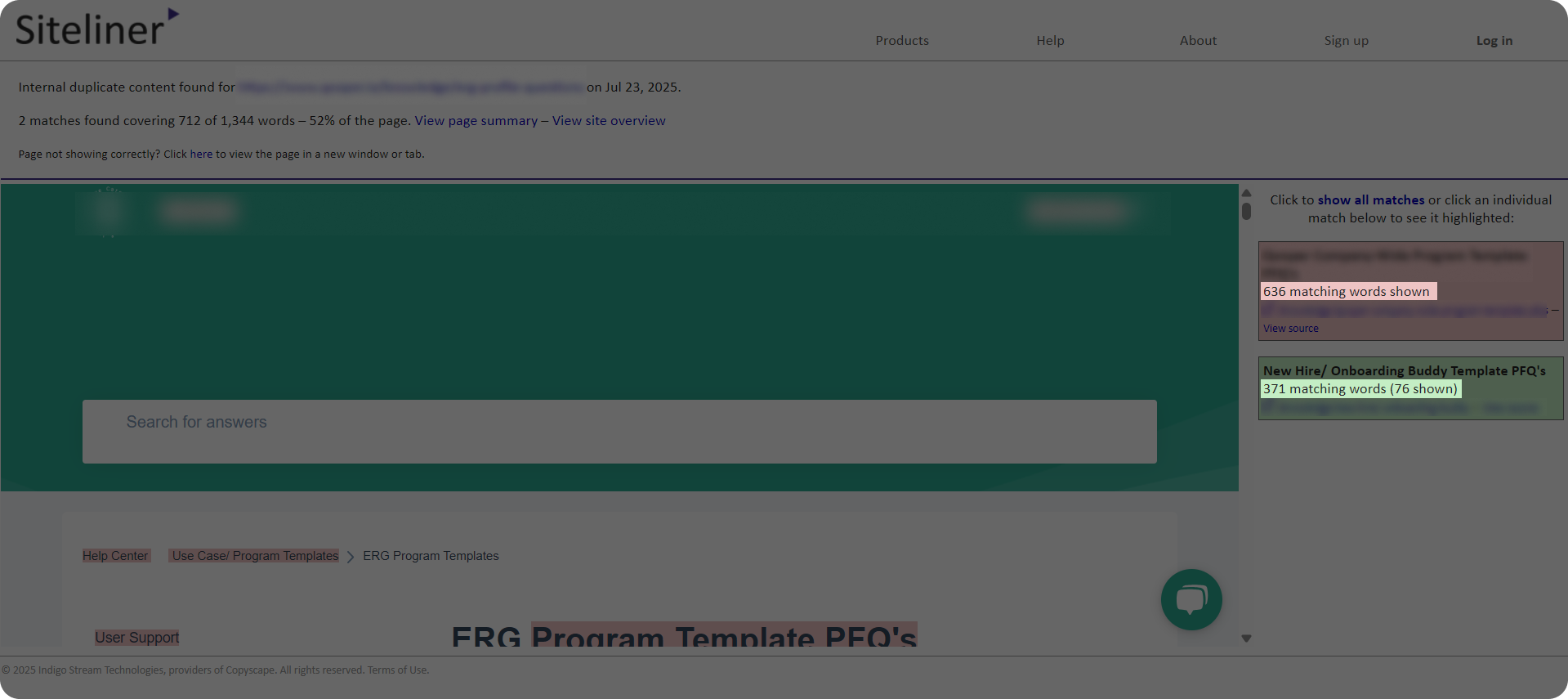
Pro tip: We recommend paying attention to pages that have more than 10% matches, since this threshold often signals a potential SEO risk.
Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog is often used by our SEO specialists for website audits.
- Type your website URL in the search bar and start crawling.
- When it’s done, in the right panel, you will see the overview of your website content with the different types of duplicates that are found. Along with exact duplicates, you’ll also see near or semantically similar content.
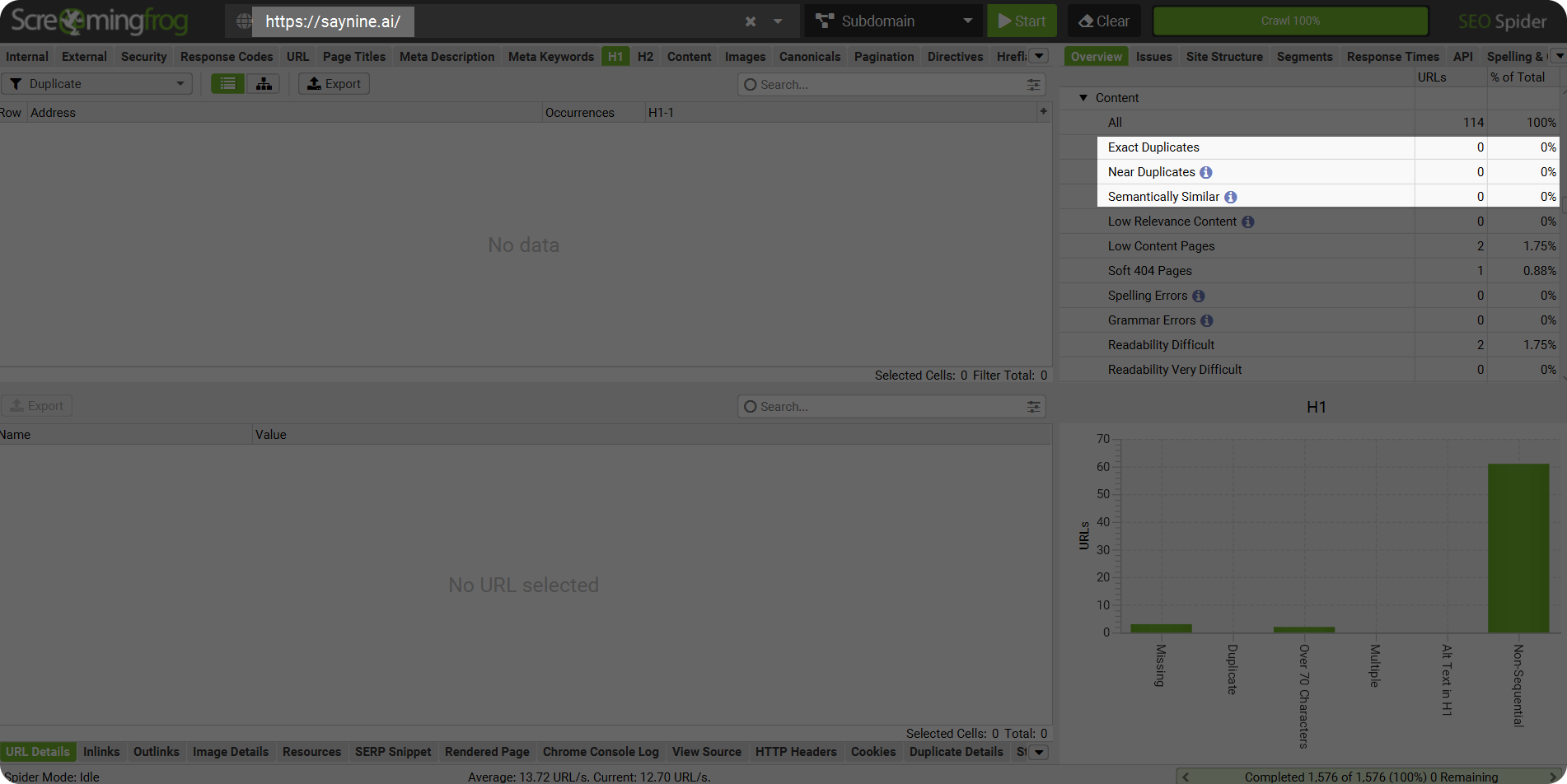
As you can see, our website has no duplicate content issue.
Now that you are a pro at finding your duplicates, it’s time to go for quick fixes.
How to Quickly Fix Duplicate Content?
Fixing duplicate content is as easy as causing it. We have gathered our expert insights and best methods for keeping your pages original and up to date.
We promise, no hard skills required.
Review and Update Your Content
Updating your content requires no specific technical knowledge. The tools we mentioned above will show you exactly which pages and sections need attention. Even the small tweaks or changes can help you avoid issues.
You can start interviewing your coworkers or industry experts to add fresh ideas to your older posts. Another way to update your content and win your readers’ trust is by adding client stories or case studies with measurable numbers that highlight your success. This type of content serves as social proof and helps maintain your brand’s authority in your niche.
Besides providing better value to your readers, content refresh also shows Google that your content is natural and worth ranking. Remember, unique and fresh ideas always catch the eye and increase your brand voice.
Pro Tip: Regularly run content audits to spot duplicate issues on time. We recommend running an audit at least once a month to keep everything clean and SEO-friendly.
Apply 301 Redirects
Once you have identified your most important pages, you can apply 301 Redirects.
It’s the process of moving an existing URL to a different one so that both users and Google understand that a page has a new location.
Imagine it like leaving your permanent address and moving to a new one. Instead of just removing the unwanted pages, you provide a simple navigation path to search engines and the website visitors.
This also prevents users from ending up on broken or removed pages, which can negatively impact the user experience.
Just make sure to redirect to a page with similar context, to provide the intended content, and avoid confusing your users.
Further reading:
Redirects for Beginners: What They Are and How to Use Them
Add Canonical Tags
Canonical tags are pieces of HTML code that prioritize your URLs for the search engines by directing them to your preferred version of the page. This is helpful if you don’t want to delete duplicate pages, but want to help Google index your desired page.
One of our clients had identical versions of their homepage. One was with “www” and the other one without it. The best solution was adding a canonical tag to a page that mattered the most.
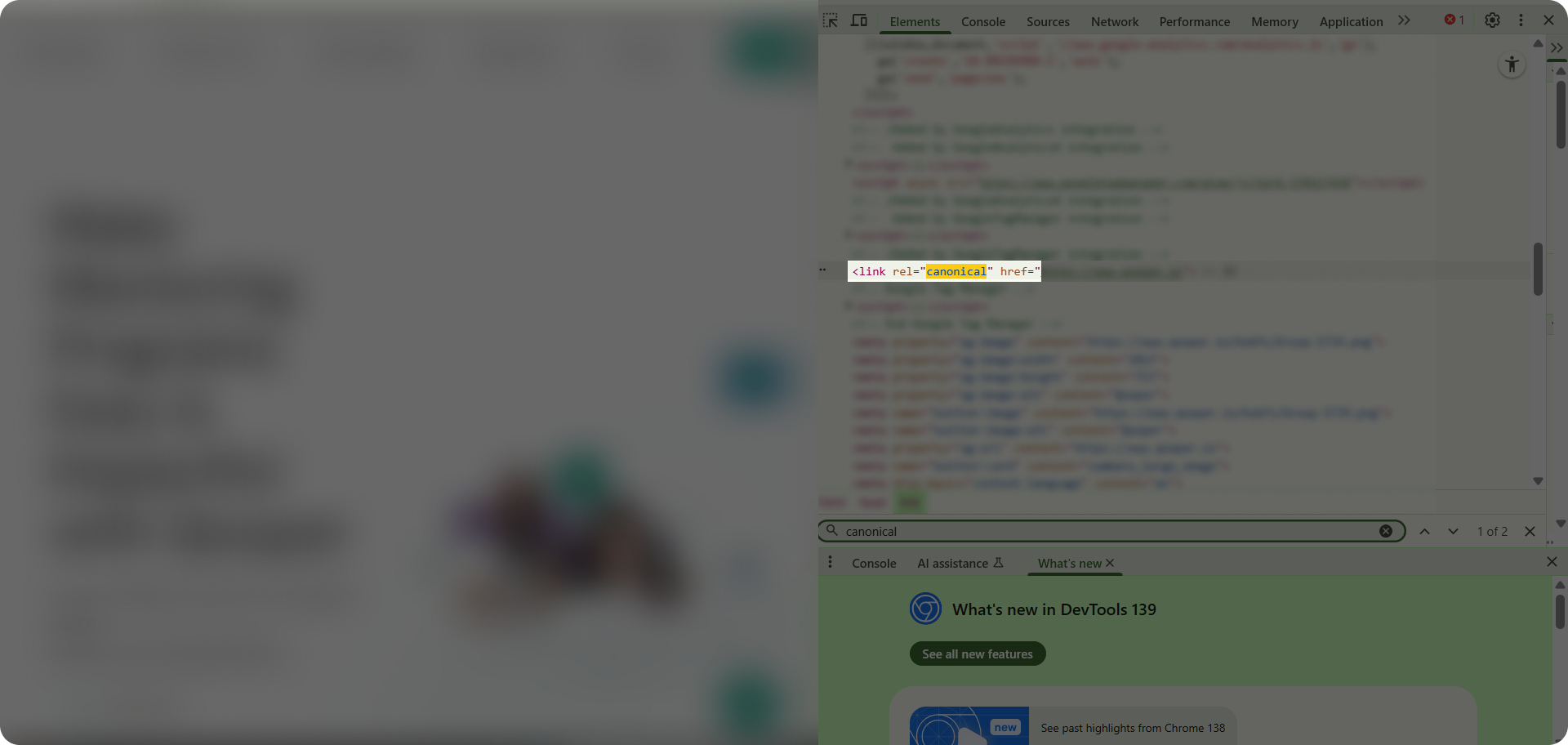
By adding a canonical tag to the client’s desired version, Google recognized it as the preferred one to index.
Further reading:
Canonical Issues: How to Fix Them
Add No Index Tags
A no-index tag does not let Google index the specific pages. Even if Google has indexed the page already, no index tags cause the search engine to deindex it.
You can use this for pages that provide the least SEO value to your website. Here is how you can add no-index tags in WordPress.
- Go to the WordPress admin panel and click on the “Posts” tab
- Select your desired article and click “Quick edit.”
- From the “Robot Meta” panel, check the “No index” checkbox.
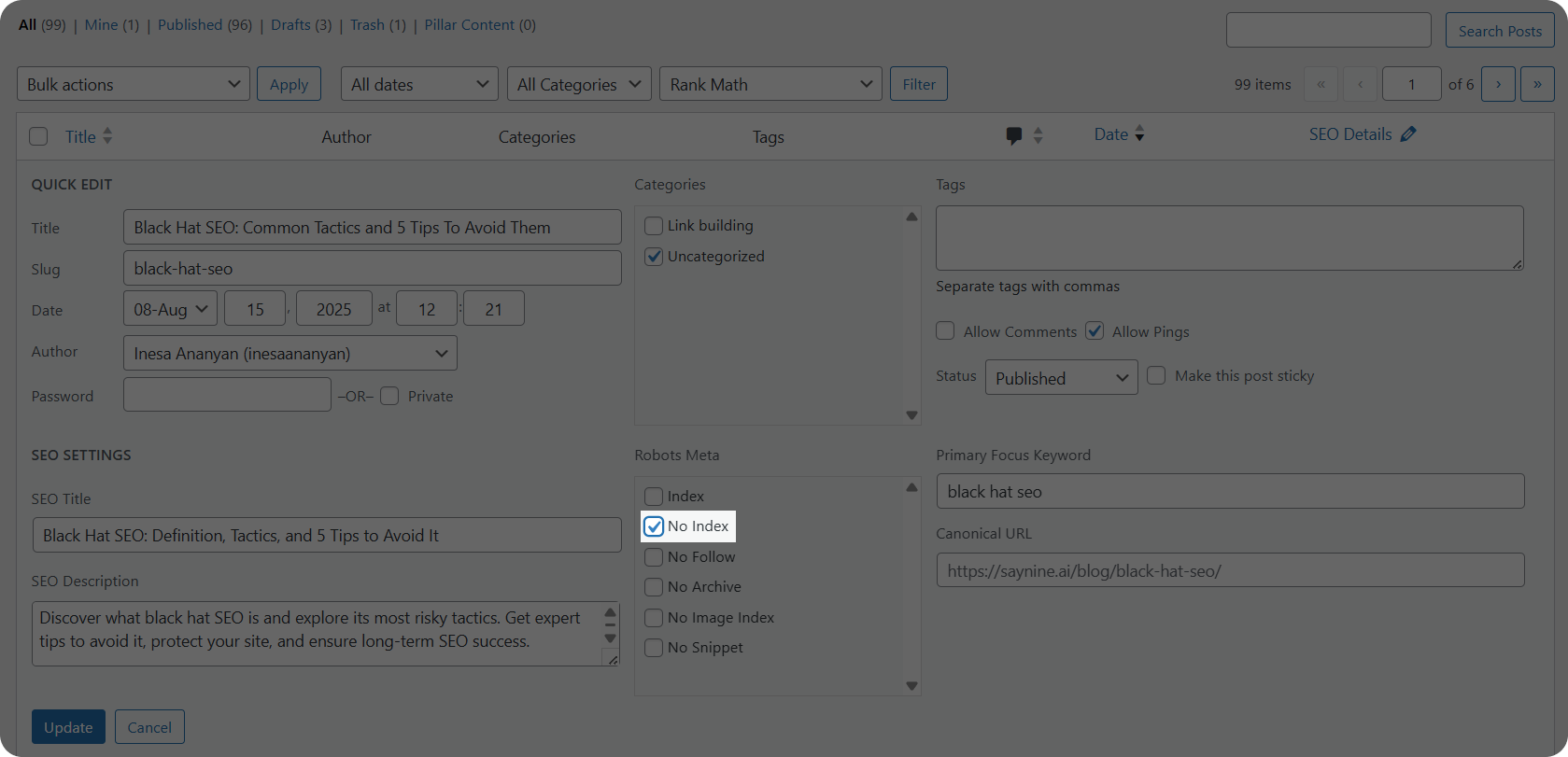
This trick makes the page temporarily invisible to Google. You can also use this for the older pages that you haven’t yet managed to update. Once updated, you can remove the tag and add the “index” tag again.
Pro tip: If you want to make the page invisible for Google, you can apply the “robots.txt” rule to your URL, which will disallow the search engine from crawling it.
Closing Thoughts
Before you go, let’s do a quick wrap-up of what we covered.
Duplicate content can silently hurt your SEO, even if your website seems to be perfectly optimized. It confuses search engines, drops your rankings, and leaves your important pages unnoticed.
Luckily, there are free tools to run content audits and find your duplicates. To prevent issues, focus on doing regular content updates, implementing redirects, canonical tags, or no-index tags.
If you’re busy or need extra help, our SEO audit services will come in handy! We provide website audits that help us reveal not only duplicate content but also other sneaky issues that negatively affect your site’s performance.
FAQ about duplicate content
How do you best describe duplicate content?
Duplicate content is when the same or very similar content shows up on more than one webpage on your website.
What is duplicate content audit?
A duplicate content audit refers to identifying and analyzing identical or very similar content appearing on multiple URLs on your site.