Internal and external links may seem identical, but they serve very different purposes. One keeps users navigating through your site, the other connects your content to the wider web and builds your authority.
Most websites get this balance wrong, and it costs them traffic, rankings, and credibility. However, it’s easy to fix once you understand the basics.
In this guide, you’ll learn the difference between internal and external links, why they matter for SEO, and how to use them effectively in your content.
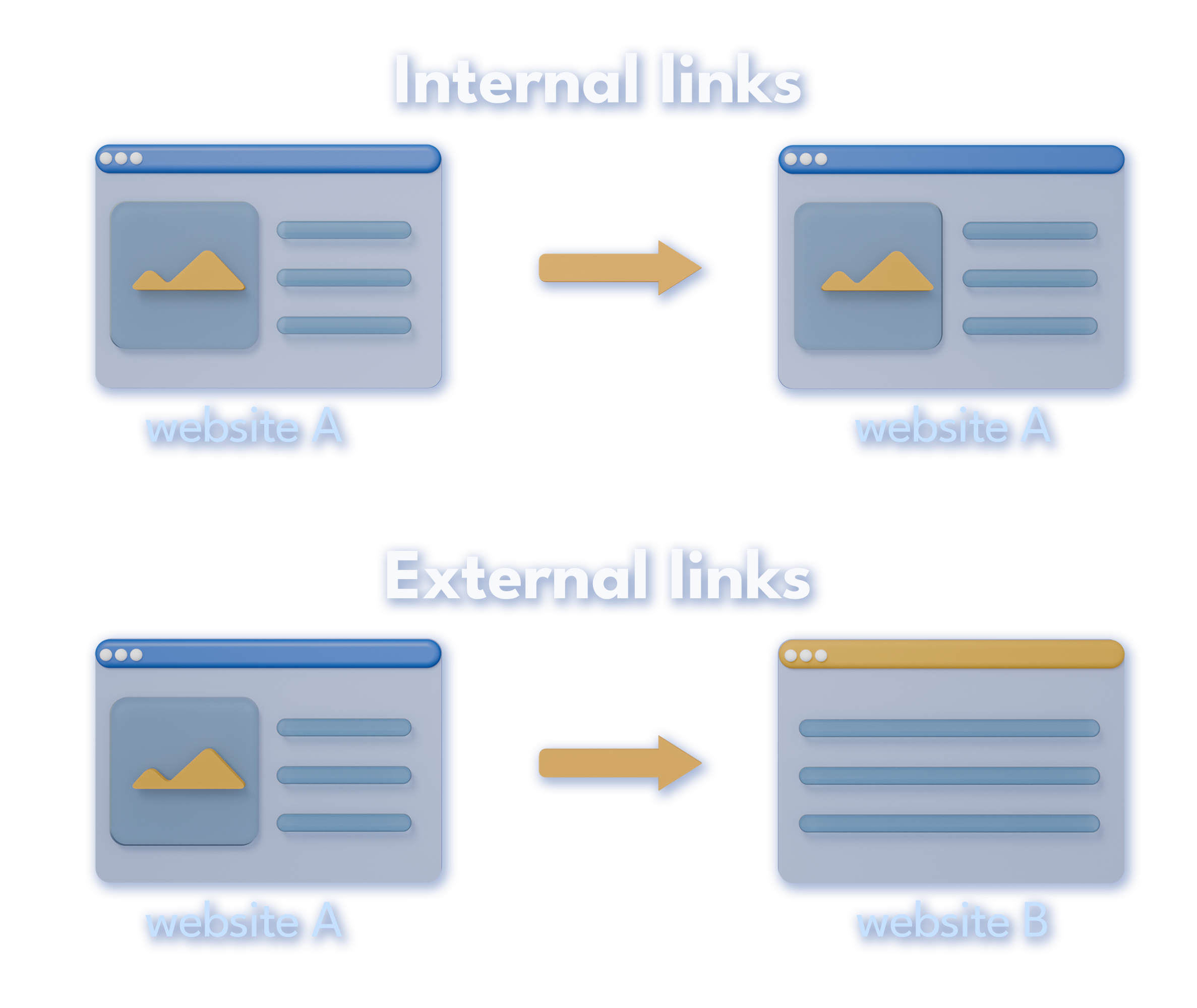
What are Internal Links?
Internal links are links that lead users from one page to another on your website.
There are different types of internal links, such as navigational links in the main menu or sidebar, contextual links (often placed in blogs), footer links, and more.
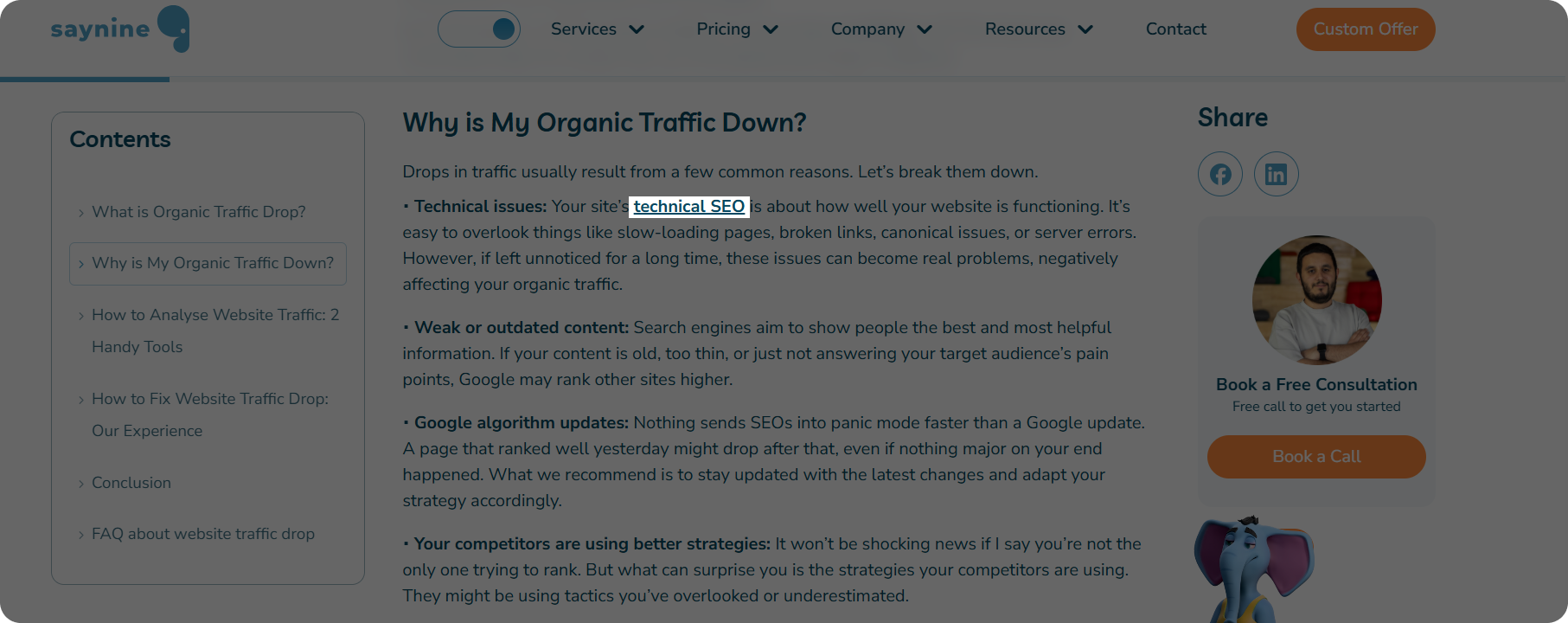
Here’s an example of an internal on a live article:
The link we added points to another blog on our website.
Further reading:
Internal Linking: Tips & Best Strategies
How to Find Internal Links to a Page
There are many options when it comes to checking internal links to a specific page.
Method #1: The Manual Way
One of the easiest and quickest ways to check internal links to a page is to do it manually.
All you have to do is go through the page and check all the links to see where they’re pointing.
However, if you need to check hundreds of pages, it’s better to use special tools to save time and focus more on important things.
Let’s explore some of them.
Method #2: Ahrefs
Take these easy steps to find all your internal links:
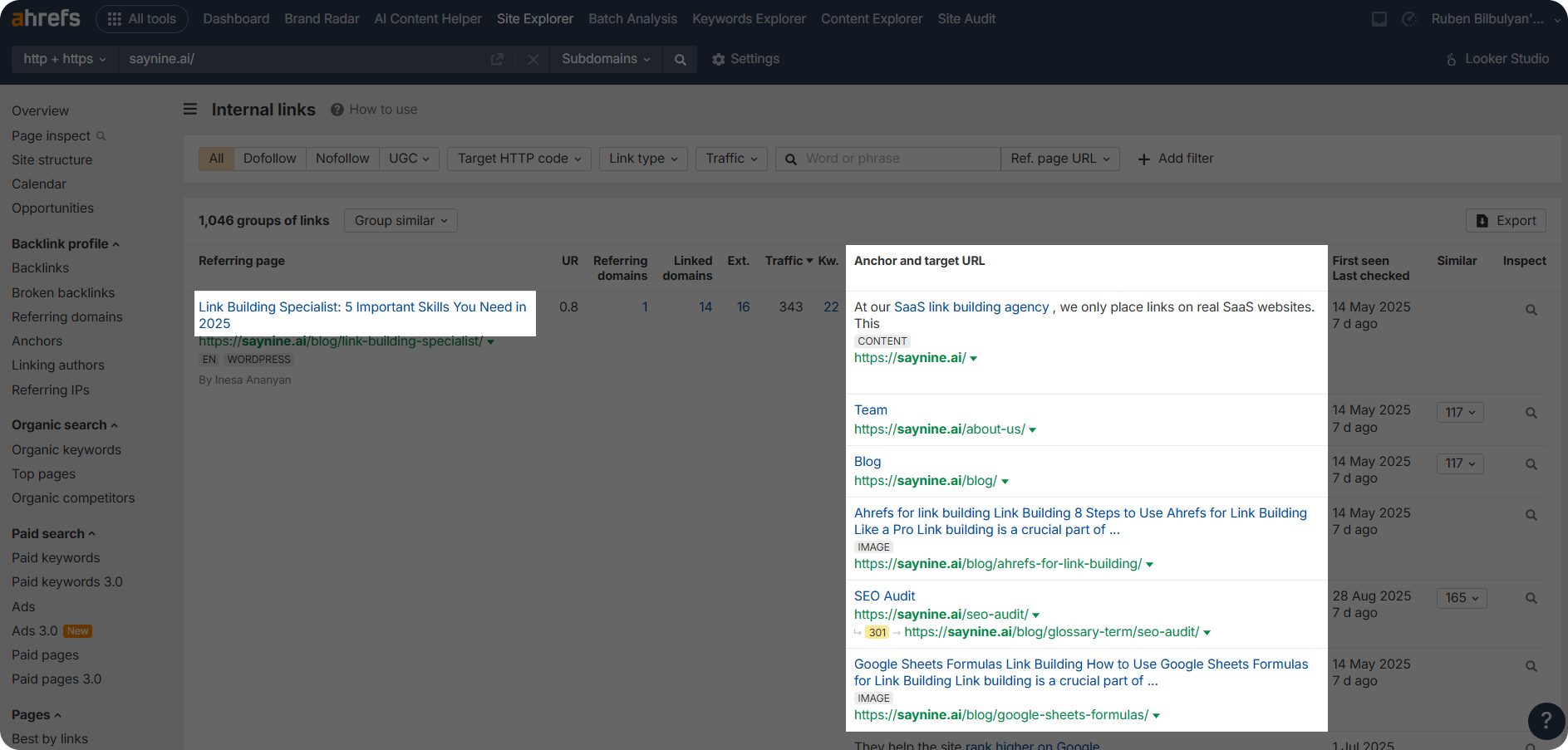
Step 1: Go to Ahrefs Site Explorer and type in your domain (e.g., saynine.ai)
Step 2: Next, find and click “Internal links” from the left sidebar.
Step 3: Here, you can see a referring domain (aka linking internal page) and all the internally linked pages on the right side.
Step 4: You can also go to “Most linked pages” to see which pages on your site have the most internal links. This tells you which pages are getting the most attention and helps you find pages that might need more links to be easily discovered.
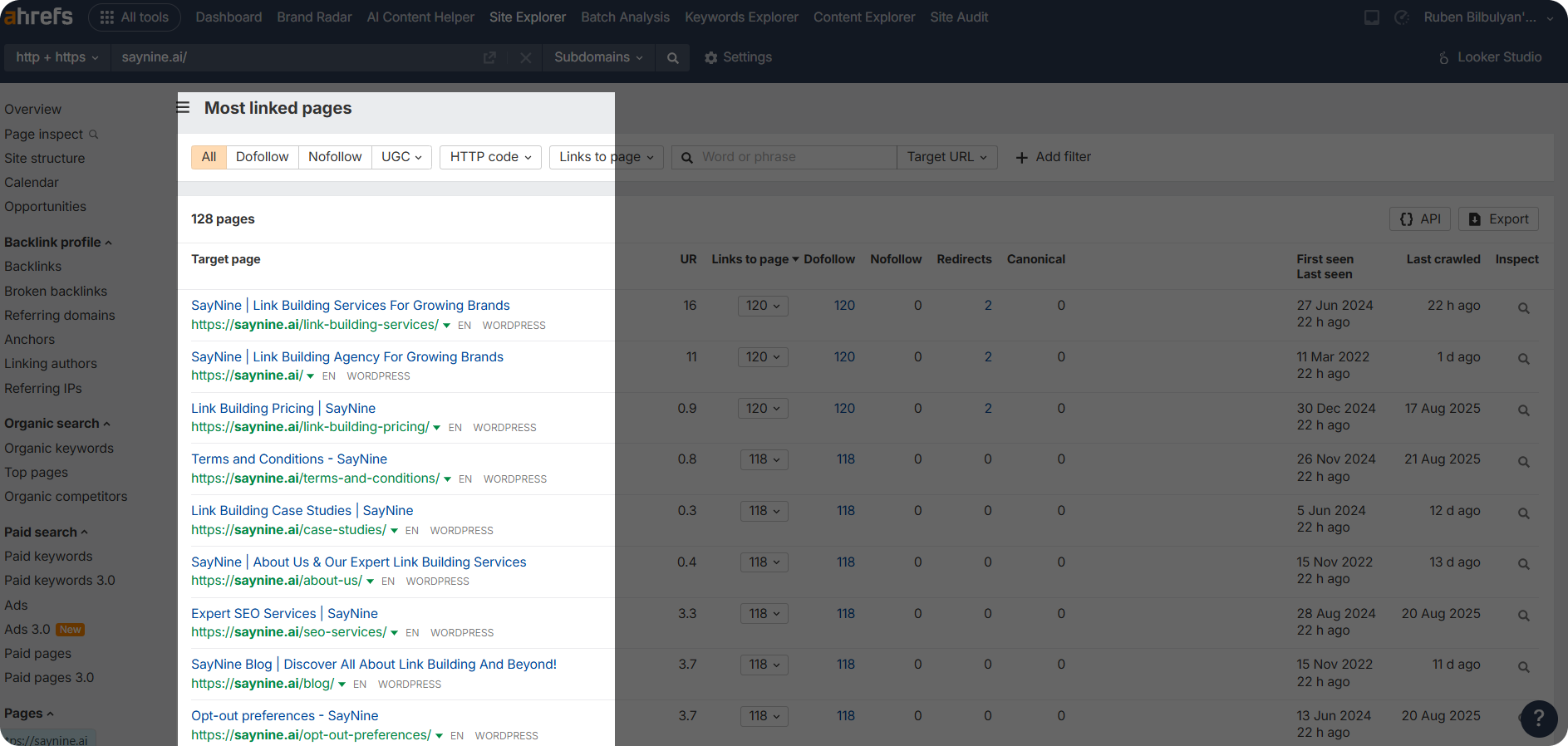
What are External Links?
External links are links that lead users to a page outside the website.
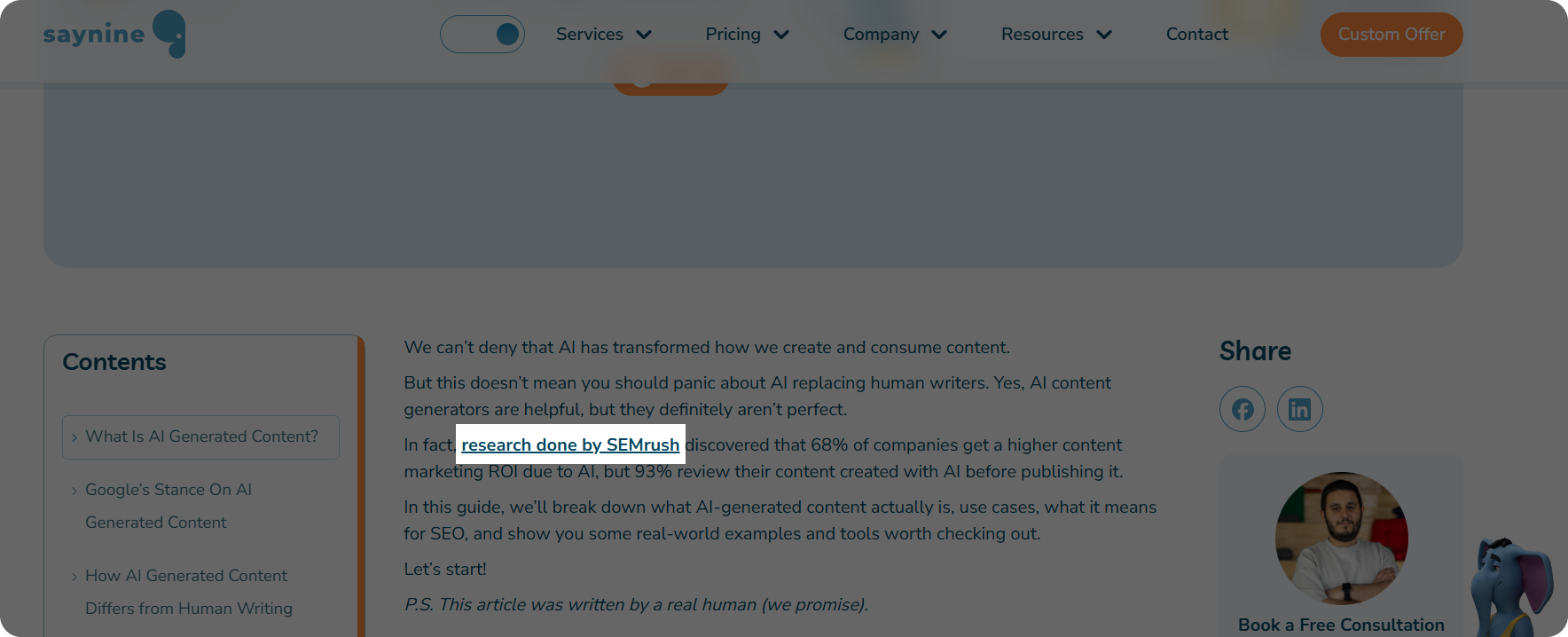
Here’s an example of an external link on a live article page.
The link points to SEMrush’s website, where users can explore all the details about the research on AI-generated content.
Ok, enough with definitions. Now, let’s learn how to check all your external links.
How to Check External Links in 3 Easy Ways
Method #1: The Manual Way
We’re big fans of automation, but sometimes it’s easy and more reasonable to do things by hand.
In this case, you can simply check your external links manually.
To check external links manually, open the page you want to review and go through the links one by one to see where they point. This helps you quickly find broken links, outdated resources, or pages that no longer make sense to link to.
Method #2: Ahrefs
To find all your external links, follow these steps.
Step 1: Type your domain into Ahrefs’ “Site Explorer”
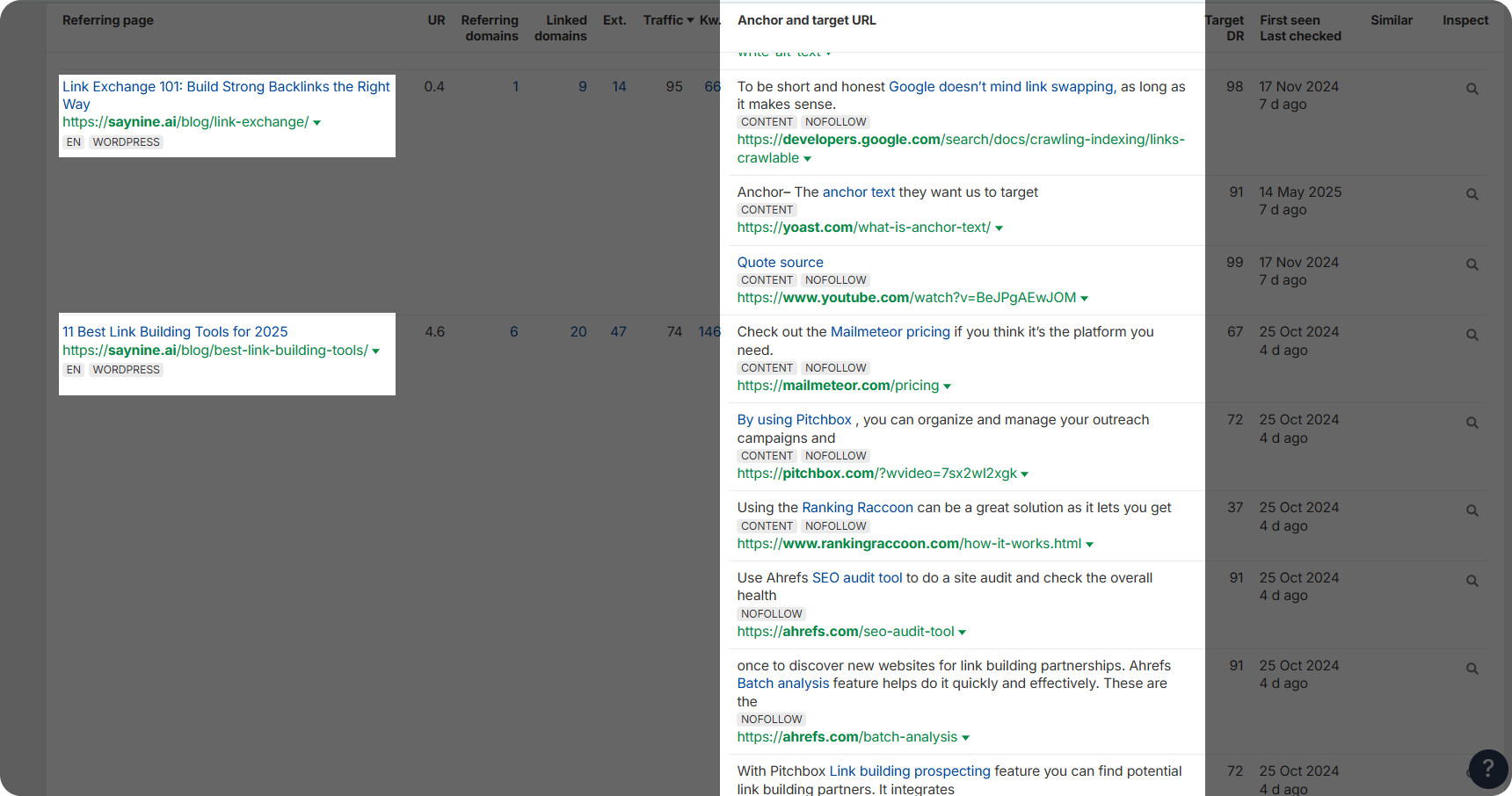
Step 2: Find and click “Outgoing links” from the left sidebar. Here you can see all your pages and their external links.
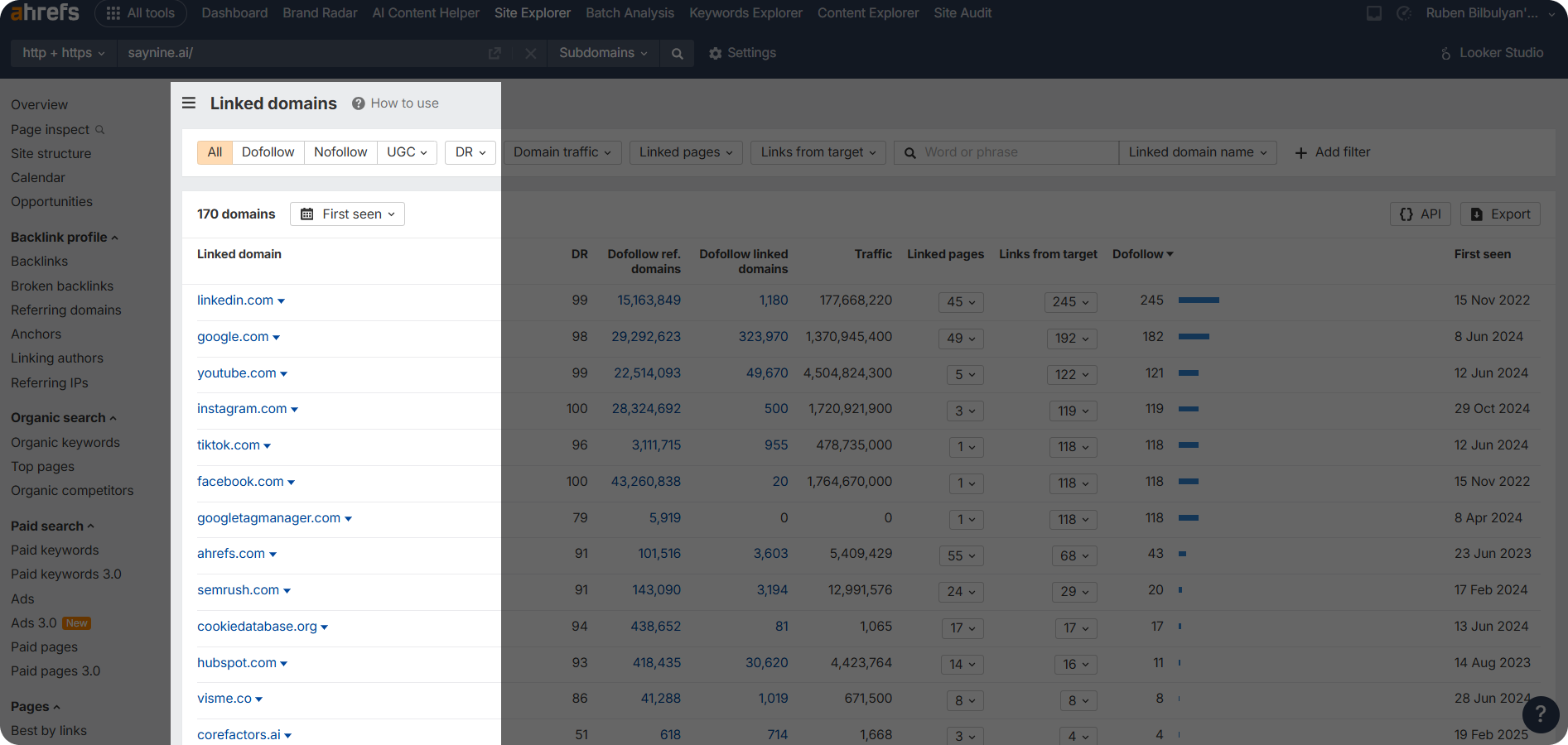
Step 3: Click “Linked domains” to see all the websites you’ve externally linked to. Here, you can set filters (e.g., DR and traffic) to identify possibly spammy domains.
Step 4: Manually review all the links to make sure they are working and lead to fresh, relevant sources.
Method #3: SEO Link Highlighter Extension
Want an even faster way to check all your external and internal links? No problem.
There’s a Chrome extension that can scan a page for both internal and external links in seconds, saving you time.
Here’s how to use it.
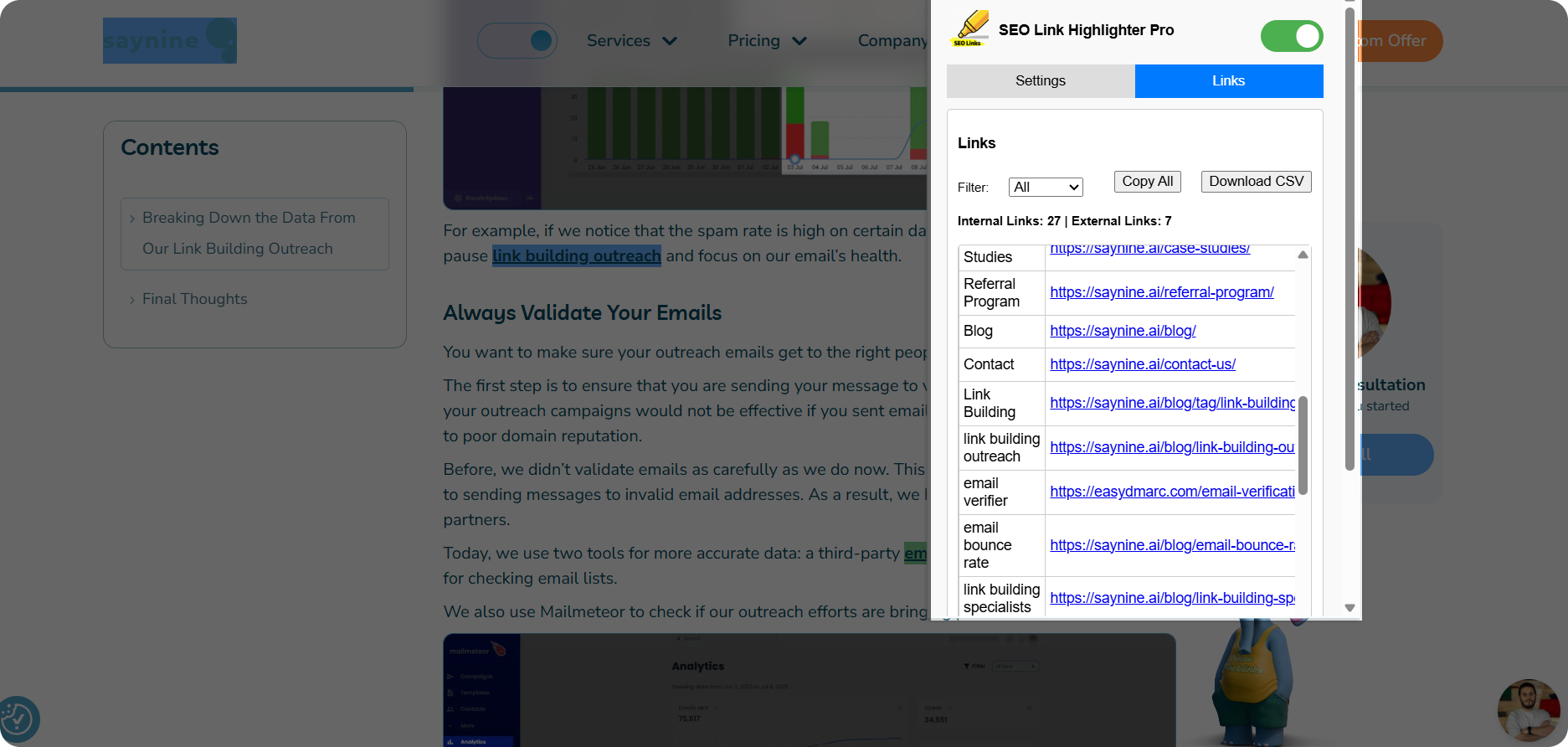
Step 1: Install the free SEO Link Highlighter extension from the Chrome Web Store.
Step 2: Go to any page you want to check and analyze all the links.
Step 3: Review all the internal links highlighted in blue and external links highlighted in red.
Step 4: To make things even easier, you can either copy all information about links or simply export as a CSV file for further external and internal link analysis.
Why Are Internal and External Links Important for SEO?
Internal and external are both essential elements when it comes to on-page optimization.
Let’s review how each of them can benefit your SEO strategy.
So, what are the SEO benefits of adding internal links? They help by:
- Making it easier for people to navigate through your site and explore more of your content,
- Helping search engines understand and index your pages faster,
- Passing link equity. If you have a page that ranks well, linking from it to a weaker page shares some of that SEO value and helps the latter perform better,
- Making sure there are no “orphan pages” without any links pointing to them.
And what about external links? Are external links good for SEO? The short answer is yes. When used right, they help by:
- Showing search engines that your content is trustworthy because you link to reliable sources, leading to increased credibility,
- Giving readers extra information or resources that make your content more helpful.
In short, both internal and external links in SEO are important. The key is using the right strategies to avoid overloading your pages with unnecessary or irrelevant links and to make sure each link adds additional value for your readers.
Internal and External Linking: Best Practices
Here are some simple tips from our SEO team to help you get the most out of your external and internal linking strategy.
- Use clear and varied anchor texts: Avoid relying on exact match anchor texts. Instead, we recommend using variations to optimize anchor texts, so they feel natural to both readers and search engines.
- Keep links relevant: Only link to pages that actually add value or help explain your topic. For example, if you’re writing a blog post about “seo tips,” link to a page that explains how to create content optimized for search engines or case studies showing successful campaigns, rather than linking to unrelated topics like email newsletter design.
- Choose fresh and credible sources: When linking to other websites, select ones that are trustworthy and up-to-date. It makes your content look more reliable and keeps readers sticking around longer.
- Place links naturally: Never force links where they obviously don’t fit to avoid keyword stuffing. Links should flow smoothly in the context so readers don’t feel distracted.
- Spread internal links evenly: Make sure all your pages are connected. Especially when writing new articles, remember to link them internally to avoid orphan pages and keep everything easily discoverable on your site.
- Audit links regularly: We recommend reviewing all your internal and external links every few months (for smaller sites) and once a month for larger ones. This way, you can easily spot bottlenecks like broken or outdated links and replace them with relevant and working ones.
Closing Thoughts
You’ve made it this far, so you clearly understand the basics of internal and external links. Now comes the fun part: putting knowledge to work.
Start small by trying one or two of our tips at first, and gradually make them part of your content strategy. Over time, you’ll get better at finding good linking opportunities.
But if you feel overwhelmed with finding or optimizing your links, we’re here to help. Our team can run a detailed SEO audit, review your site, suggest the best linking opportunities, and guide you in creating content that improves both user experience and rankings.
FAQ about internal and external links
How many internal links should a page have?
There’s no rule of thumb, but make sure to add enough links to help users navigate your site and discover related content.
What is the difference between an internal link and a backlink?
An internal link points to another page on your own website, while a backlink comes from another website to your site.