A successful website goes beyond just having a nice design—it’s about smooth functionality and strong SEO performance. But how do you know if it’s truly working at its best?
If you’re unsure where improvements are needed, this website audit checklist can help. This guide, built on insights from our SEO team, will help you analyze your site’s performance, identify problem areas, and provide strategies to fix them.
Make a copy of our free site audit template to stay organized throughout the website audit process.
Time to learn more about website audits and how to use these resources.
What is a Website Audit?
A website audit is a detailed analysis of your site’s health, typically focusing on areas like SEO, user experience, technical aspects, content, and backlinks.
By auditing a website, you can identify opportunities for improvement, make sure your site is working efficiently for better SEO results.
When and Why Do a Website Audit?
We recommend to audit your website once a month to keep things running smoothly. Regular checks help you spot problems before they become big issues.
Noticed a drop in traffic or keyword rankings? That’s your sign to run a site audit. The cause could be anything from a site issue, a Google update, or even competitors catching up.
In other words, auditing a website helps you identify what’s causing the drop and gives you a plan to get back on track. Our website analysis checklist can help you during the process to ensure you’re covering all the important aspects of your site’s performance.
Types of Website Audits
There are several key areas we focus on during an audit to make sure everything is running seamlessly and your site is optimized for SEO.
Let’s take a closer look at two main types of website audits:
Technical SEO Audit
This audit looks into the technical side of the website, checking for issues that could affect functionality. It includes identifying broken links (404 errors), server error pages, and slow page loading times.
These problems can impact user experience and hurt SEO rankings, so it’s crucial to address them quickly.
SEO Content Audit
Unlike traditional content audits that mainly assess relevancy and quality, at SayNine, we focus more on identifying duplicate content issues (which can confuse search engines) and keyword cannibalization (when multiple pages target the same keywords).
During the SEO content audits, we also focus on the small details that make a big difference for both SEO and user experience. More specifically, we review meta titles and descriptions, as well as if images and headings are properly optimized.
Getting these elements right helps search engines understand your content and gives visitors a better, more enjoyable experience.
Further reading:
Content Audit Guide
Content Optimization for SEO
If you’re looking for a hands-off approach, our monthly SEO audits can help ensure your site is always performing at its best, so you can focus more on growing your business.
Technical Audit Checklist: Key Checks & Tips
Here’s a breakdown of the essential technical checks to keep your site performing at its best.
Page Speed
Page speed refers to how quickly a web/mobile page loads and displays content. It’s a critical factor for user experience; slow loading times can frustrate visitors and increase bounce rates.
But more importantly, page speed is also a ranking factor for Google, a change they introduced back in 2010. Moreover, Google introduced the “Speed Update” in 2018, making page speed a ranking factor for mobile searches too.
So, even if your content is compelling and backlinks are excellent, slow page speeds can hurt your SEO efforts.
To check and analyze your site’s speed, consider using Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool:
Simply enter your website’s URL and click “Analyze.” Then review the diagnostics to identify areas for improvement in your page speed.
If your page speed score is low, you’ll need to dig deeper to identify the root of the issues.
Red diagnostics are priority areas that need immediate attention.
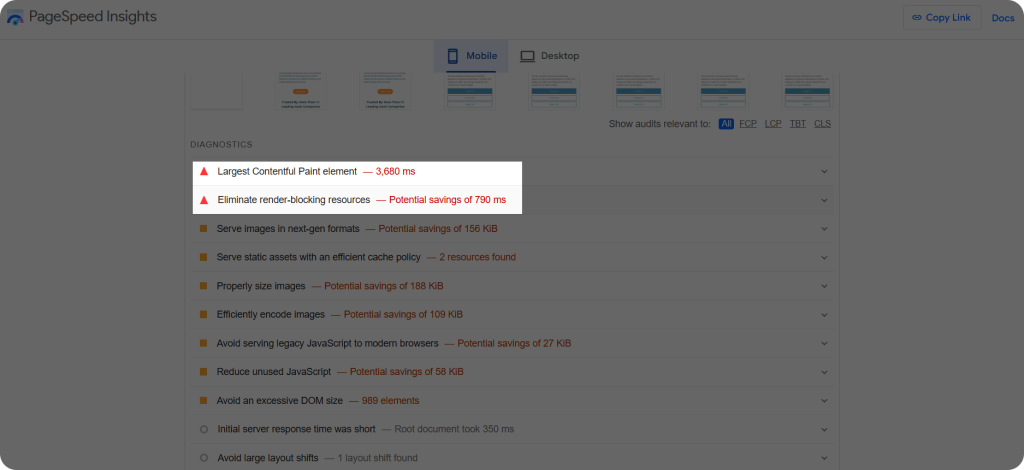
For example, when we analyzed SayNine using PageSpeed Insights, one of the key red issues for mobile optimization was the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP). This element is often the heaviest file on your site, and improving this can significantly enhance load time.
This is just one of the many factors that can affect page speed, and while it’s crucial to address higher-priority issues, even the less urgent ones should be fixed to ensure optimal site performance.
How to Fix Page Speed Issues: Our Quick Recommendations
- Identify what affects page speed and make adjustments accordingly.
- Compress images
- Assign code-related issues (like reducing unused JavaScript and CSS code) to your development team to improve the overall page load time.
The faster your site, the happier your users (and Google).
Non-Indexed Pages
Non-indexed pages are web pages on your domain that haven’t been added to Google’s search index.
Why is this an issue? These pages aren’t eligible for search rankings and won’t show up in search results. So, non-indexed pages hold no SEO value, making it important to identify and resolve them without delay.
To identify non-indexed pages, we use Google Search Console (GSC):
Step 1: Open GSC and click “Pages” from the left sidebar
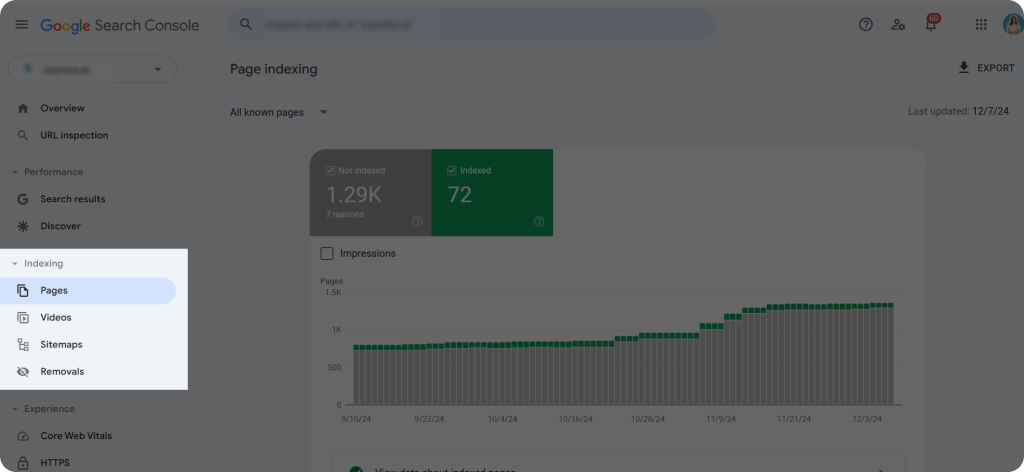
Step 2: Scroll down to “Why pages aren’t indexed” to check the reasons.
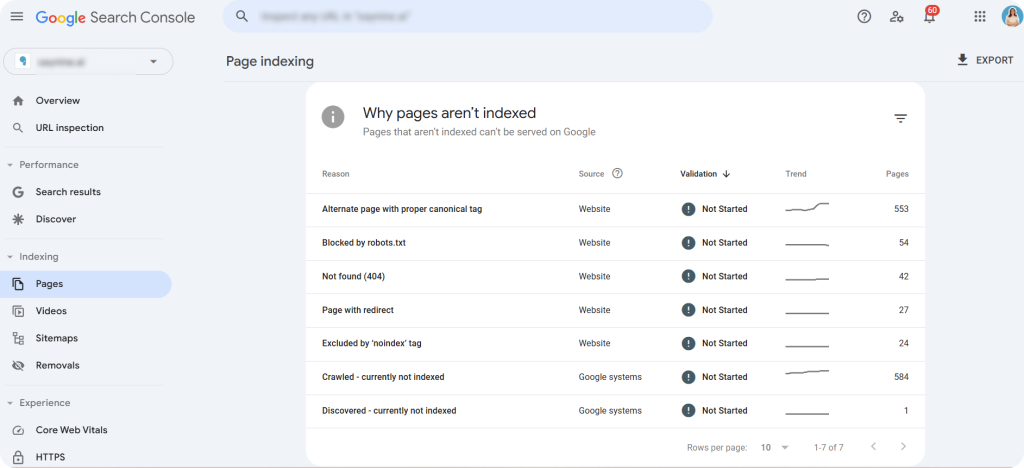
Step 3: Click on each reason to gain insights into the specific issues preventing your pages from being indexed.
For example, a “Not Found (404)” error indicates a broken page that Google eventually removes from its index after crawling it again.
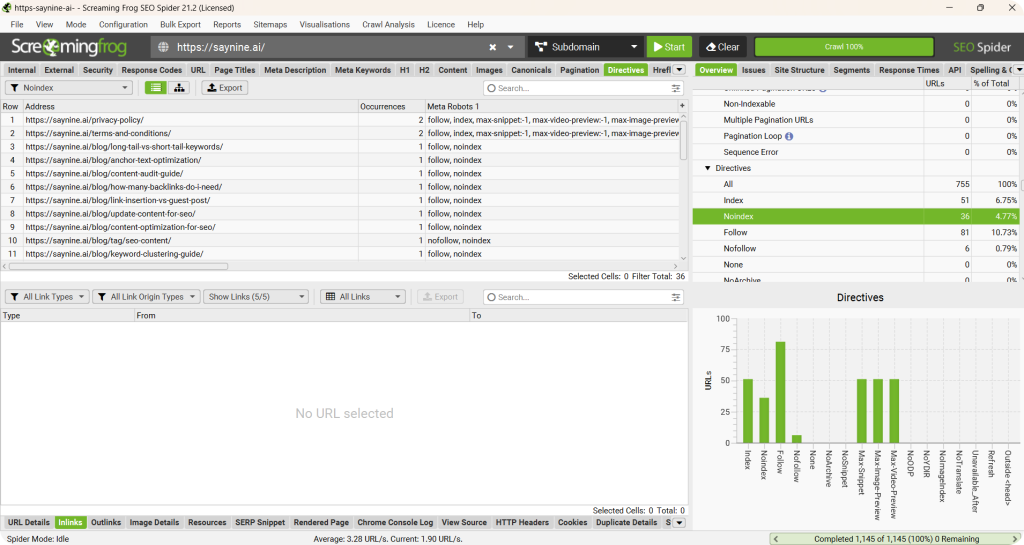
We also use Screaming Frog to find non-indexed pages. All you need to do is:
Step 1: Run a crawl of your website using the tool.
Step 2: Check the response codes to find non-indexed pages and their status.
How to Fix Non-Indexed Page Issues: Our Proven Tips
- Use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to check why a specific URL is non-indexed, and determine if the issue is technical.
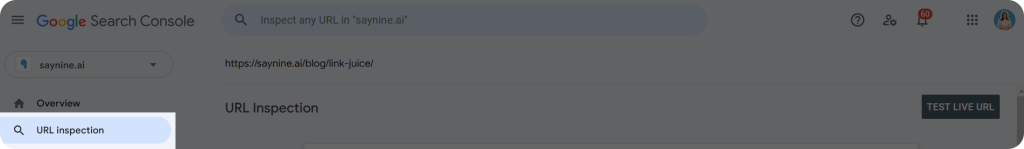
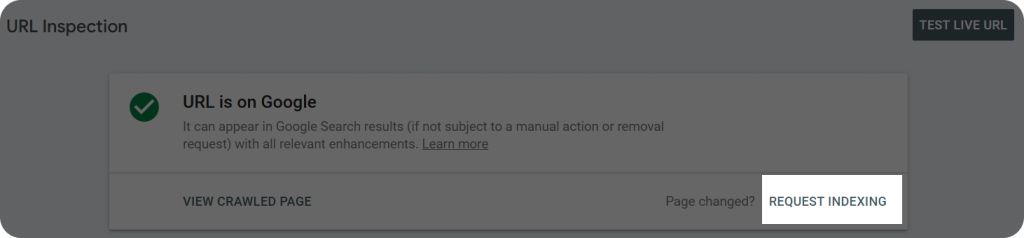
- Try manually requesting indexing through GSC to get the page back in the index.
- Use Inspect Element (Ctrl + Shift + I) to check whether the page contains a “noindex” tag. It could have been added intentionally (e.g. for underperforming pages that you don’t want to show up in search results).
Once you resolve non-indexed pages, you’ll be one step ahead to improving your site’s SEO.
Sitemaps
A sitemap is like a map for Google, including all the URLs on your website that you want to be indexed. It helps Google easily find and understand your site’s important pages.
Think of it as a guide to help search engines know which pages matter most to you, which can lead to better visibility and improved rankings over time.
It’s also worth mentioning that every website has a “crawl budget,” which refers to the number of pages Google can crawl within a given timeframe. A well-optimized sitemap can help increase this budget.
When auditing a website, we check a site’s sitemap using three methods.
- Manually: We can check any site’s sitemap by typing domain/sitemap.xml on the search bar.
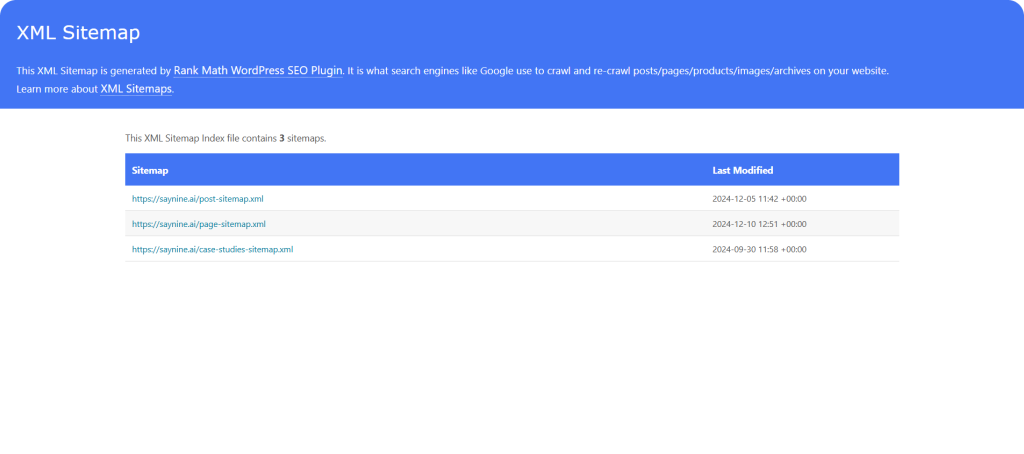
Note: If you’ve added a “no index” tag to any pages, they’ll be automatically removed from your sitemap.
- Through Robots.txt: Another way is by looking at domain/robots.txt to see what pages Google is allowed to crawl.
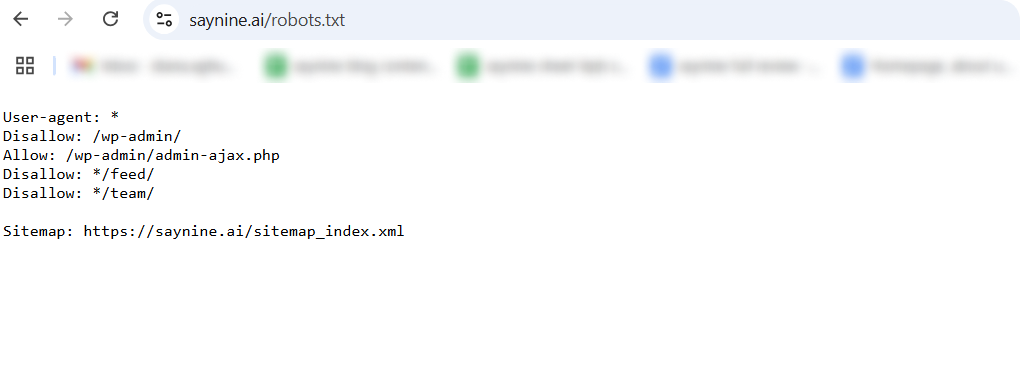
If your site has a sitemap, it will be here.
- Use Google Search Console:
Sign in to your GSC account and click on “Sitemaps” from the left sidebar.
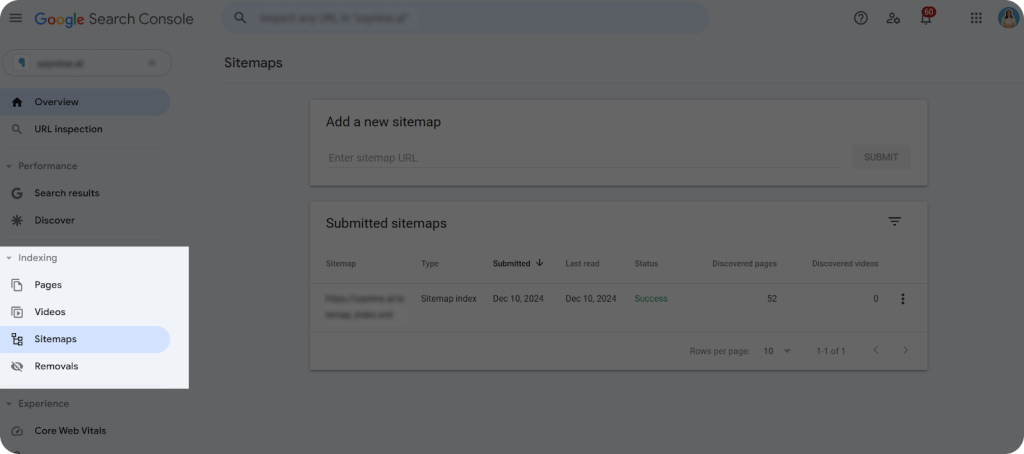
Here, you can find information about when your sitemap was last crawled, when it was submitted, and monitor its status.
Sitemap Essentials: Best Practices from Us
- Include only working URLs and important pages you want to be indexed in your sitemap.
- Avoid broken links or “no index” pages to protect your SEO.
- Use tools like Yoast SEO, RankMath, Screaming Frog, or XML-Sitemaps to create a sitemap.
- Refresh your sitemap periodically to keep it up-to-date.
So, keep your sitemap fresh, and Google will love crawling your best pages!
Robots.txt
A robots.txt file is a tool that helps you control which pages Google and other search engines can crawl and index on your website.
When Google visits your site, the first thing it checks is your robots.txt file. This tells Google which pages are a priority for crawling and indexing.
Without it, Google might crawl and index all pages, even the ones you don’t want, which could negatively affect your SEO.
To check any site’s robots.txt, we use two methods.
- Manually: Simply type your domain/robots.txt into the search bar and click Enter.

Here’s what your robots.txt looks like, but let’s explain some of the terms in the screenshot.
- User-agent*: This means that we don’t want any search engine bots to crawl and index our pages.
- Disallow: Tells Google which pages it should not crawl.
- Allow: Tells Google which pages it can access.
The next method is using Google Search Console:
Sign in to your GSC accounts and head to “Settings “ from the left sidebar.
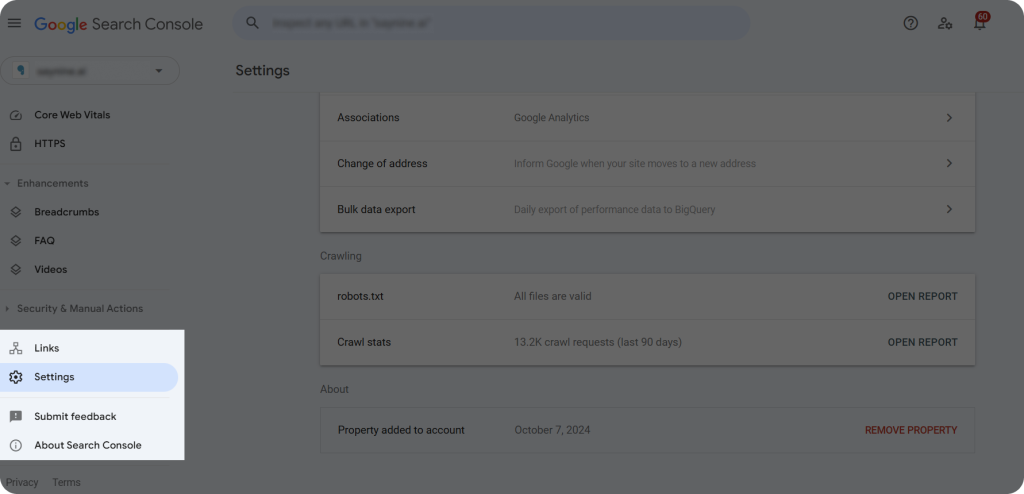
Simple Robots.txt Best Practices
- Disallow sensitive pages like admin pages for data security.
- Create and submit your robots.txt file using any text editor like Notepad, then upload it to your server and integrate it into Google Search Console for testing.
By properly setting your robots.txt, you can ensure Google focuses only on the right pages and avoids those that aren’t meant for indexing.
SEO Content Audit Checklist: Essential Checks & Best Practices
Understanding how to do a website audit means uncovering content-related issues like duplicate content and keyword cannibalization.
So, follow these must-do checks to ensure your content is optimized for better search rankings.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to pieces of content that appear in more than one place on the web, either within the same website or across multiple websites.
While having duplicate content doesn’t lead to penalties, it can still harm your SEO. For instance, Google may struggle to decide which version of the content to rank higher. This can lead to lower rankings, reduced traffic, and even deindexing of duplicate pages.
We recommend using Siteliner to check duplicate content on your website. Here’s how:
Simply enter your domain into Siteliner and review the list of pages that contain duplicate content.
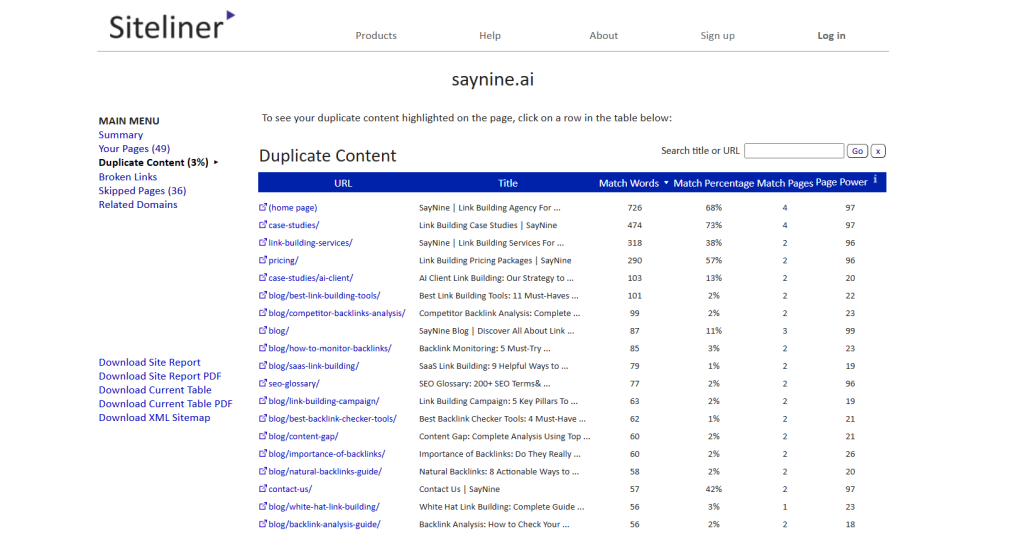
As you can see in the screenshot above, Saynine.ai has 3% of duplicate content, which is low.
When you click on any URL, you’ll be able to see which other page(s) share the same content. Any duplicate content will be highlighted in red for easy identification.
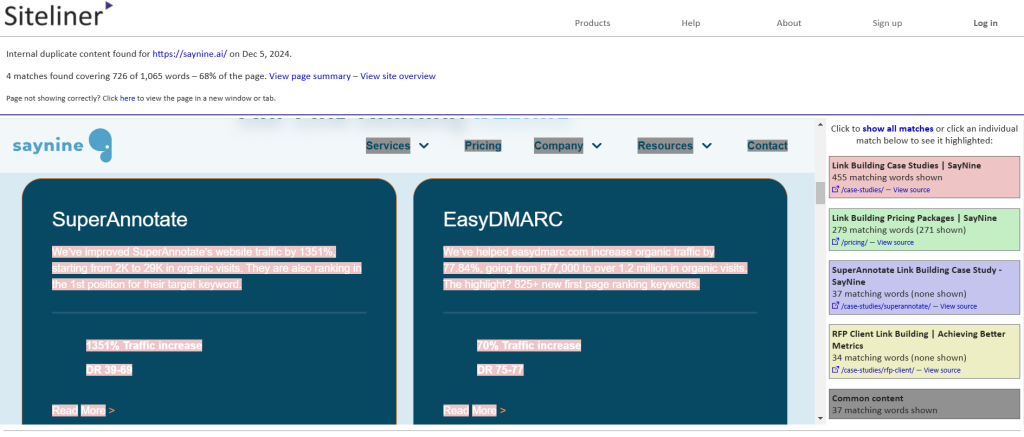
But what to keep in mind when it comes to duplicate content?
- Not all duplicates are bad: For instance, footer and header content or pricing info are generally not considered duplicate issues by Google, even if the tool flags them.
- Don’t ignore small percentages: Even if the tool shows a 30% duplication, it’s worth investigating. Sometimes, it’s just a duplicated paragraph, and cleaning it up can make a big difference.
- 10% duplication is generally acceptable, but the lower the percentage, the better.
If you find that your site has duplicate content, we suggest doing the following:
- Little duplicacy: Update and rewrite the content to make it more unique.
- 100% duplicate content: Consider adding a “noindex” tag to less important pages to prevent them from showing up in search results.
- 301 Redirects: If a page isn’t important, consider redirecting it to a more relevant, higher-priority page using a 301 permanent redirect.
- Canonicalization: If you have similar content across multiple pages (like “saynine.ai” and “saynine.ai/”), use a proper canonical tag to tell Google which version to prioritize.
Taking care of duplicate content means clearer, more effective SEO that won’t be slowed down by redundant or competing pages.
Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization is when multiple pages on your website target the same or very similar keywords.
Instead of helping each page rank better, these pages end up competing with each other, which can confuse search engines like Google, resulting in lower rankings for both pages.
To check if your site is suffering from keyword cannibalization, we suggest using Google Search Console and following these steps:
- Log in to your GSC account and head to the “Performance” tab from the left-hand sidebar.
- Scroll down to the “Queries” section, which shows the keywords your pages are ranking for.
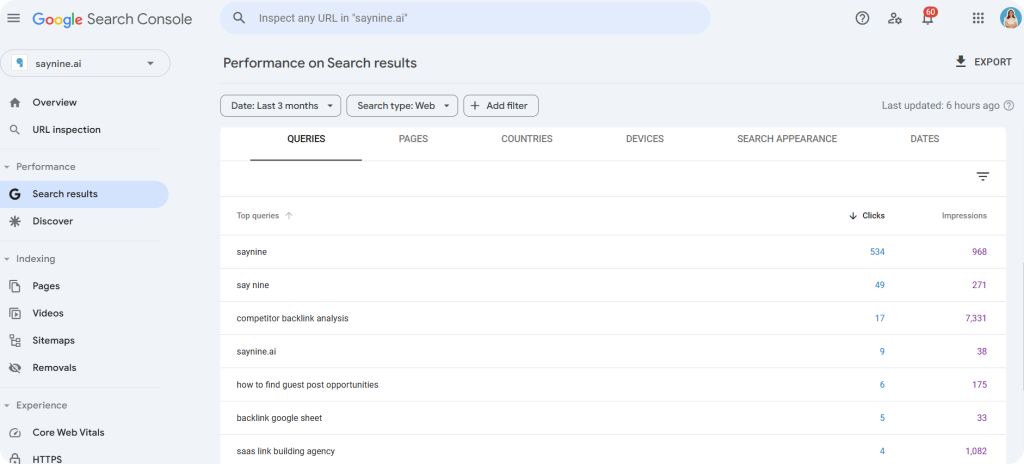
- Click on keywords to see which pages rank for them. If they’re competing for the same spot, you’ve found a case of cannibalization.
But how to avoid keyword cannibalization? We highly recommend to:
- Use keyword clusters to target unique clusters and avoid overlap
- Monitor keywords to spot cannibalization on time
- Ensure each page targets a distinct search intent, so pages don’t compete for the same queries
- Use anchor texts for internal links in the right way
Avoiding keyword cannibalization will enable your website to achieve higher rankings, make better use of your content, and provide a more seamless experience for both search engines and users.
Meta Tags
Meta tags, which are your meta title and meta description, are HTML elements that help search engines and users understand the content of your webpages.
A page title, or meta title, is an HTML component that indicates the title of a web page, which you can see highlighted in the screenshot below.

Meta descriptions, on the other hand, are short summaries of a webpage’s content, typically displayed under the meta title in search engine results.
Why they matter, you may ask?
- First, they help search engines better understand what your page is about.
- Second, the clearer and more effective your meta tags are, the higher the chances users will click on your pages.”(more clicks = more traffic and more conversions).
However, meta tags can be imperfect too, and doing regular checkups can help you reveal issues like missing meta titles or duplicate meta descriptions.
What we recommend is to:
- Regularly review your meta tags, either manually or with tools like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog.
- Ensure meta titles are 50-60 characters and meta descriptions are 150-160 characters for optimal display.
- Write meta tags that are descriptive, clear, and compelling to engage users and improve click-through rates.
By keeping your meta tags in check, you make sure your pages are more visible and clickable in search results, leading to both increased rankings and user engagement.
Heading Tags
Heading tags play a crucial role in your content’s structure and SEO performance, which is why we make them a priority during content audits. They serve as a roadmap for readers and search engines, helping both understand the hierarchy and main points of your page.
When auditing a website content, we check for:
- Missing or Duplicate Headings: Each page should have only one H1 that clearly defines the main topic.
- Concise headings: Stick to headings up to 70 characters to keep them clear.
- Subheading Structure (H2s and H3s): We always recommend our clients to include H2s and H3s in their content to create a logical flow and enhance readability. Plus, subheadings are also a great way to strategically include different types of keywords, both primary and secondary.
Headings might seem minor, but, in fact, they’re a major player in your content’s success. So, keep them concise, structured, and SEO-optimized to make an impact.
Images
Images play a crucial role in SEO. They not only make your content visually appealing, but also improve accessibility and help search engines understand your pages better. However, poorly optimized images can hurt your site’s performance.
When conducting an SEO audit, here’s what we pay attention to:
- Alt Texts: Every image should have an alt text that accurately describes it to help search engines understand the content of the image better.
- File Size: Images larger than 100 KB can slow down your site. While minor overages aren’t a big issue, having many oversized images can negatively impact page speed.
Our recommendations:
- Compress Images: Use tools to reduce file size without compromising quality.
- Add Alt Texts: Keep them concise and under 100 characters for clarity and SEO benefits.
By following these steps, you ensure that images contribute positively to your SEO strategy without negatively affecting performance.
Internal & External Links
Both internal and external links are critical elements of an SEO strategy.
Internal links connect different pages within your website. They improve navigation, lead to more helpful content. They also play a crucial role in indexability—if you’ve published new content, linking it internally helps Google find and index it faster.
External links, on the other hand, are links leading to a page outside your website. They’re also crucial for indexability—when you link to an external source in your article, Google can discover your content even if your blog hasn’t been indexed yet, thanks to the external link pointing to your page.
To ensure you’re using internal and external links effectively, we use Ahrefs during the audit. Here’s how we and you can also check your links:
Step 1: Sign in to Ahrefs and select your project under “Site Audit.”
Step 2: Click on “Links” to review both internal and external links.
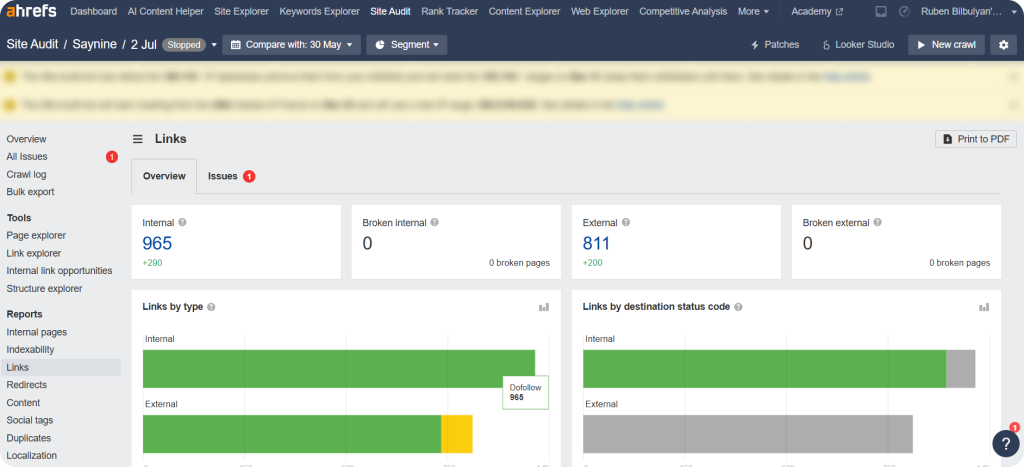
Step 3: Click on “Issues” to learn more about any internal or external link problems on your site.
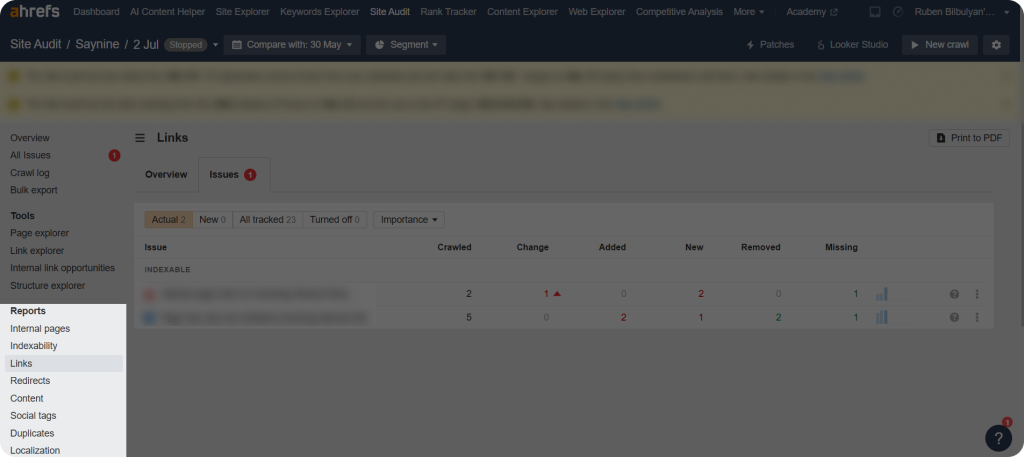
As shown in the screenshot, this site has minor issues (e.g., orphan page) that still need to be addressed for proper indexing.
Here’s what we recommend when it comes to internal and external linking:
- Add internal and external links if they’re missing.
- If you have too few links, consider adding more.
- Optimize anchor text to be relevant and clear.
- For external links, always link to trustworthy websites that add value to your content.
Optimizing your links is a small task that comes with big SEO rewards—so, keep them strategic.
Website Audit Example: Addressing Duplicate Content
Let’s walk you through a real example of auditing one of our client’s site for duplicate content using Siteliner.
The site’s overall duplicate content percentage is 10%. While this may seem a minor problem, a closer look reveals a page with a 100% match, which is definitely a red flag.
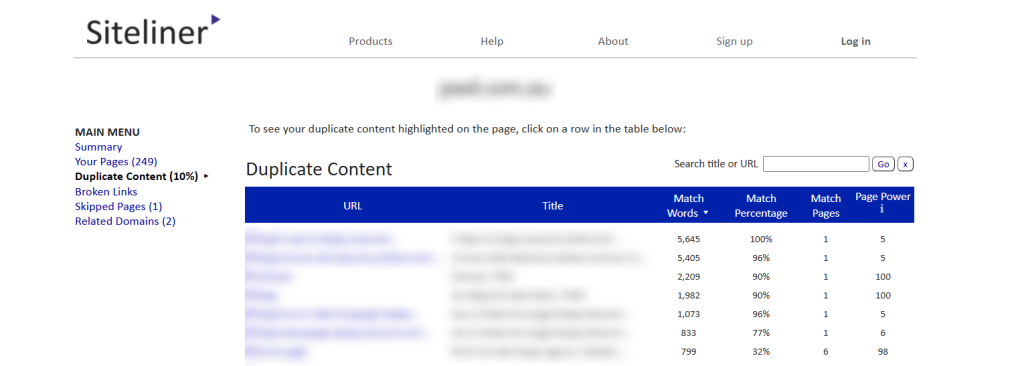
By clicking the URL, we confirmed the content was entirely identical to another page’s content.
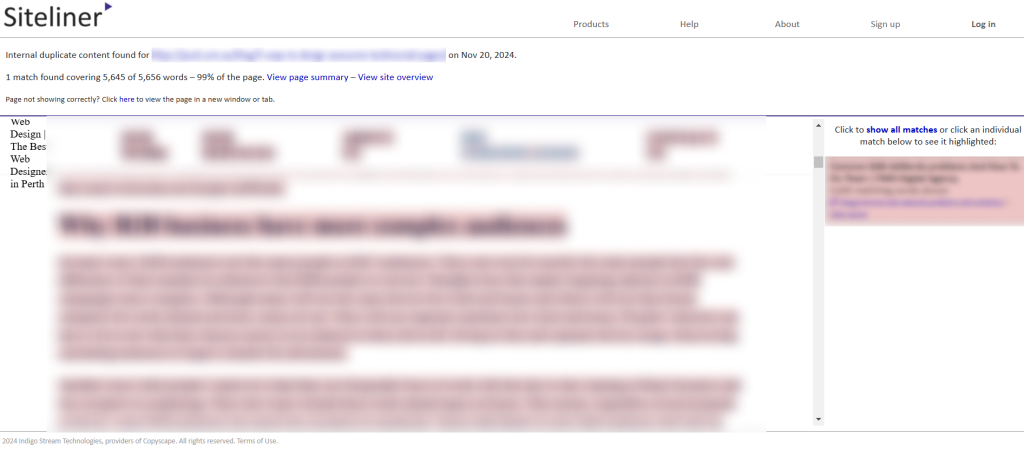
In this case, we can offer three solutions:
- Canonicalization: Adding a canonical tag to prioritize one page.
- Content Updates: Updating one page’s content to make it unique and apply a no-index tag to a less critical page.
- 301 Redirect: Redirecting the less relevant page to the more important one.
This approach ensures better SEO health and avoids penalties.
7 Best Website Audit Tools
Take a look at our top picks, all tried and tested to ensure your website’s success.
Siteliner
Siteliner is a website analysis tool that allows to identify key problems affecting your site’s performance and search engine rankings.
We love it, as it’s easy-to-use and the valuable insights about duplicate content or broken links it provides with one click.
Key Features:
- Provides XML sitemap
- Duplicate content detection
- Broken link checker
- Page power analysis
- Detailed Siteliner reports
Pricing:Free for sites up to 250 pages; Premium version is also available, allowing up to 30,000 pages with more frequent analysis. Check out their website for more pricing information.
Google Search Console
A must-have tool for tracking your website’s performance on Google’s search results.
We use it primarily for tracking search performance of our clients’ important pages, as well as, for identifying non-indexing issues.
What makes this tool great? Let’s take a look at its main features.
Key Features:
- Tracking search performance (e.g. impressions, clicks, average CTR, etc.)
- Monitoring indexing status of a site’s pages
- URL inspection tool
Pricing: Google Search Console is free.
Ahrefs
Ahrefs’ Site Audit tool offers powerful website audits and helps us identify issues like broken links, indexability issues, duplicate pages, content issues, etc.
The tool’s user-friendly design is great for beginners. Plus, it offers accurate data and plenty of features for advanced users.
We also love how Ahrefs continuously improves its tool, keeping us updated with new features and alerts.
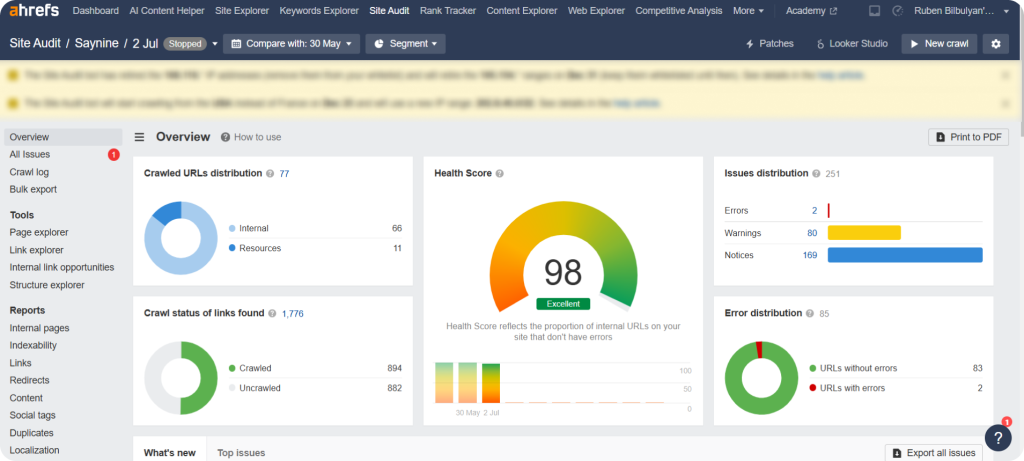
However it comes with other features too, which you can find below.
Key Features:
- Backlink analysis
- Keyword research
- Content Explorer
- Competitive analysis
- etc.
Pricing: The Lite package starts at $129/month. Ahrefs also offers Standard, Advanced, Enterprise packages, as well as solution for beginners. Check out their website for more pricing info.
Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog is a popular desktop app and a great website audit tool for identifying SEO issues such as broken links, redirects, and missing metadata.
What we love about this tool is that it helps identify important technical issues and get suggestions on how to fix them.
Key Features:
- Site crawl for SEO issues
- Duplicate content analysis
- Redirect and broken link checker
- Identifying canonicalization issues
- Identifying hreflang issues
Pricing: Free (up to 500 URLs). Paid plans start at $259 Per Year.
SEMrush
SEMrush offers a range of SEO audit tools, including Site Audit tool, which helps us conduct site performance checks.
What we love about it is its accurate data and how it presents audit results in a visually appealing way, which makes analyzing complex data much simpler.
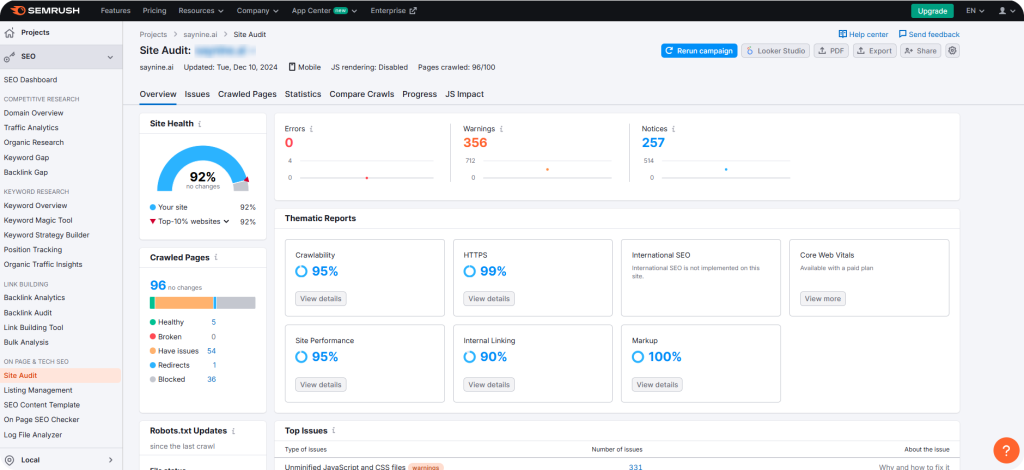
Apart from its Site Audit tool, you may also want to check out some other features of SEMrush.
Key Features:
- Competitor analysis
- Keyword tracking
- Position tracking
- Backlink audit
- Backlink analytics
- On-page SEO checker
- etc.
Pricing: Paid plans start at $139.95 monthly.
PageSpeed Insights
PageSpeed Insights (PSI) evaluates the user experience of a webpage on both mobile and desktop devices and offers helpful suggestions to enhance its performance.
Its user-friendly interface makes it easy for us to find page speed issues, understand core web vitals, and implement all the necessary changes for a smoother and faster browsing experience.
Key Features
- Website speed analysis
- Mobile optimization insights
- Performance score
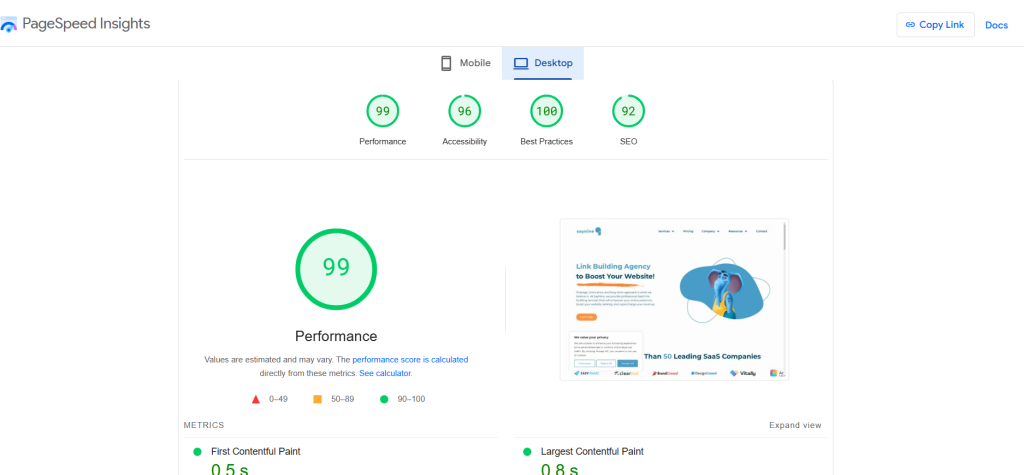
Pricing: PageSpeed Insights is free.
Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a great tool for tracking visitor behavior on your site and getting insights into performance metrics.
It goes beyond what Google Search Console provides by offering detailed information about where clicks come from, for example, and how users engage with your site.
Key Features:
- Traffic tracking
- In-depth performance metrics
- User engagement data
- Device optimization insights
Pricing: Google Analytics is free.
Stay Optimized with Regular Website Audits
Let’s wrap up all the essential things you need to know about website audits.
- A website audit is a detailed evaluation of your site’s performance, concentrating on areas such as SEO, user experience, technical issues, content, and backlinks.
- It’s recommended to audit your website once a month to ensure smooth performance, and catch potential issues early.
- A technical SEO audit identifies website issues like errors and slow loading, while an SEO content audit focuses on duplicate content, keyword cannibalization, and optimizing meta tags for better SEO and user experience.
- A technical SEO audit includes checks for page speed, non-indexed pages, sitemaps, and robots.txt files to ensure fast loading, proper indexing, and optimal search engine crawling.
- An SEO content audit involves checking for issues like duplicate content, keyword cannibalization, missing or poorly optimized meta tags, headings, images, and internal/external links to improve rankings and user experience.
And don’t forget to download our free template to make the website audit process even simpler!
Thanks for reading!
FAQ about Website Audit Checklist
What is included in a website audit?
A website audit typically includes assessment of technical elements, on-page SEO, content quality, link structure, website speed, and user experience.
How to do a SEO audit for a website?
To do an SEO audit, you’ll need to review your site’s technical performance, content quality, backlinks, and device optimization using tools like Google Search Console, Google Analytics, Ahrefs, or SEMrush.
How long does a website audit take?
It depends on your website’s size. A small website usually takes 2-3 hours for a full audit of health and performance.
What is a website content audit?
A website content audit is a review of your site’s content to see what’s working, what’s not, and how it can be improved for SEO and your audience.
How do I create a website audit report?
To create a website audit report, assess key areas like technical and content issues, use a checklist or template to organize findings.
How to do technical audit of a website?
Check site speed, crawlability, and indexing issues using tools like Google Search Console and Screaming Frog. Fix broken links and optimize load times for better SEO.

Quiz Time
Let's put your knowledge to the test.
Leave your email below to get a SayNine certificate!
Are you sure?







